Definition:
Cell (in biology), the smallest functional unit of an organism. Including prokaryotes and unicellular (bacteria) or eukaryotes (protists), a microscopic usually consist of a single cell, while the objects multicellular (metazoans) made of many of cells together in specialized groups.
Cell (in biology), the smallest functional unit of an organism. Including prokaryotes and unicellular (bacteria) or eukaryotes (protists), a microscopic usually consist of a single cell, while the objects multicellular (metazoans) made of many of cells together in specialized groups.

We can be divided into two main types of cells in terms of size and internal organization: procaryotic cells and protozoa. Among eukaryotes, plant
and animal cells, however, are very close, through its infrastructure.
There
are many arguments, including morphological and chemical, it was found that
these cells are the origin of all living organisms, animals or plants, and
derived from the same primitive cell - of life.
Characteristics:General characteristics:
Although many of their differences in appearance and function, all cells have a number of common characteristics: surrounded by a membrane (called the plasma membrane) contain rich material in the area of water and cytoplasm. Plasma membrane defines the boundary between inside and outside the cell. All cells also contain the genetic information contained in DNA to form chromosomes that carry genes. DNA controls the activities of the cell and allow him to play in the treatment of its properties to its descendants, from cell division, which is the basis of heredity.
Differences:
Cell is the basic unit of all living organisms. Sometimes, a single cell is an organism that is the case of single-celled bacteria and eukaryotes (protists). All other organisms (metazoans) is composed of many cells. And usually these specialized and have different morphologies and according to their function.
Although Mjhrathaamoma (there are exceptions, such as bacteria namibiensis Thiomargartia, measuring 0.75 mm, egg Ookhlih, and with a diameter measured in centimeters) in size and shape variables. Smaller than bacteria (prokaryotes), with size typically between 0.5 and 100 microns - micron (1 micron = 1000 of a millimeter) - but some nanobacteria, does not exceed 0.2 microns. Bacteria and many different forms, and stick in spherical الحليزين, and so on. Maintained by the stomach wall surrounding the plasma membrane. Some whip wear longer than 20 micrometers on average.
Plant cells as a particular form (usually rectangular or polygonal), granted by a wall of cellulose. And have a size between 20 and 30 micrometers on average. Fungal cells are similar, but surrounded by a wall of cellulose, but chitin. Animal cells are not static: surrounded by the plasma membrane by any wall. Maintain the overall shape of the fiber cytoskeletal (contractile protein network reflect the cytoplasm), and also their movements as possible. The size is usually between 10 and 20 microns.
Characteristics:General characteristics:
Although many of their differences in appearance and function, all cells have a number of common characteristics: surrounded by a membrane (called the plasma membrane) contain rich material in the area of water and cytoplasm. Plasma membrane defines the boundary between inside and outside the cell. All cells also contain the genetic information contained in DNA to form chromosomes that carry genes. DNA controls the activities of the cell and allow him to play in the treatment of its properties to its descendants, from cell division, which is the basis of heredity.
Differences:
Cell is the basic unit of all living organisms. Sometimes, a single cell is an organism that is the case of single-celled bacteria and eukaryotes (protists). All other organisms (metazoans) is composed of many cells. And usually these specialized and have different morphologies and according to their function.
Although Mjhrathaamoma (there are exceptions, such as bacteria namibiensis Thiomargartia, measuring 0.75 mm, egg Ookhlih, and with a diameter measured in centimeters) in size and shape variables. Smaller than bacteria (prokaryotes), with size typically between 0.5 and 100 microns - micron (1 micron = 1000 of a millimeter) - but some nanobacteria, does not exceed 0.2 microns. Bacteria and many different forms, and stick in spherical الحليزين, and so on. Maintained by the stomach wall surrounding the plasma membrane. Some whip wear longer than 20 micrometers on average.
Plant cells as a particular form (usually rectangular or polygonal), granted by a wall of cellulose. And have a size between 20 and 30 micrometers on average. Fungal cells are similar, but surrounded by a wall of cellulose, but chitin. Animal cells are not static: surrounded by the plasma membrane by any wall. Maintain the overall shape of the fiber cytoskeletal (contractile protein network reflect the cytoplasm), and also their movements as possible. The size is usually between 10 and 20 microns.

Cell bodies of different types of cells and thus usually smaller than 30 microns. However, some cells may be a very long extension of the cytoplasm.
Thus, the hair roots of plants,
and can each of which represents a continuation of the cell, to several centimeters long.
In animals, axons,
and the extension of nerve cells (neurons), can be up to several meters (a giraffe, a whale ...).
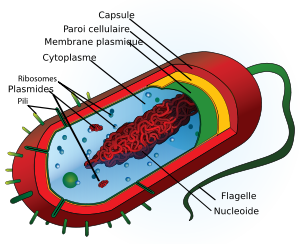
Compared with eukaryotic cells,
and prokaryotic cells have a very
simple structure. It
does not contain organelles, and all biochemical reactions carried out by elements (enzymes,
ribosomes, and protein)
in solution in the cytoplasm.
Similarly, the genetic material is free
in the cytoplasm to form a chromosome, and the circular one. A lot of germs,
but, as a small additional tracks of DNA, and also circular,
called plasmids.
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes:
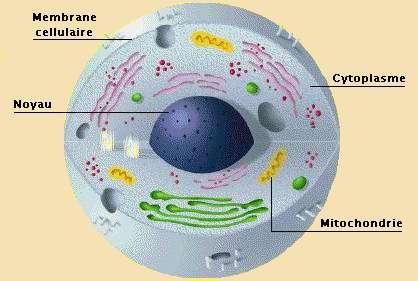
In eukaryotes the contrary, and genetic material, and consist of several chromosomes stick, and enclosed in a structure called the nucleus, which is surrounded by a double membrane, the nuclear membrane. This fundamental difference has been building eukaryotic words, "a real nucleus" and procaryotic "by the nucleus." Moreover, and eukaryotic cells contain membrane surfaces large: is fragmented all cellular functions into force and carried out by specialized structures, each surrounded by a membrane, organelles.
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes:
In eukaryotes the contrary, and genetic material, and consist of several chromosomes stick, and enclosed in a structure called the nucleus, which is surrounded by a double membrane, the nuclear membrane. This fundamental difference has been building eukaryotic words, "a real nucleus" and procaryotic "by the nucleus." Moreover, and eukaryotic cells contain membrane surfaces large: is fragmented all cellular functions into force and carried out by specialized structures, each surrounded by a membrane, organelles.

Plant and animal
cells and fungal cells:
Plant cells, fungi and animals eukaryotes and very close in structure. Differences lie mainly in the lining that surrounds (or not) the plasma membrane and the presence or absence of chloroplasts. The plant cell is surrounded by a wall and rigid cellulose molecule (which does not exist), and contains, in addition to all the organelles common to other eukaryotes, chloroplasts capable of photosynthesis. Moreover, the cytoplasm largely occupied a large cavity. These cells are surrounded fungal strict wall of chitin (a protein found in insects, for example) and other characteristics are those of animal cells. This, without a wall, and chloroplasts. In small gaps and scattered in the cytoplasm.
Plant cells, fungi and animals eukaryotes and very close in structure. Differences lie mainly in the lining that surrounds (or not) the plasma membrane and the presence or absence of chloroplasts. The plant cell is surrounded by a wall and rigid cellulose molecule (which does not exist), and contains, in addition to all the organelles common to other eukaryotes, chloroplasts capable of photosynthesis. Moreover, the cytoplasm largely occupied a large cavity. These cells are surrounded fungal strict wall of chitin (a protein found in insects, for example) and other characteristics are those of animal cells. This, without a wall, and chloroplasts. In small gaps and scattered in the cytoplasm.


No comments:
Post a Comment