Start now to review the
first meiosis:A)
prophase I Prophase:This
mode is similar to its counterpart in the division indirect but stay longer and
characterized into several stages, including: -Phase 1 Alqladah:
LeptoteneThis
stage begins nucleus and intensify inflation chromosomal material and the start
of the central body composition very short strings radialThen
look chromosomes Kckheot extremely long and thin organized swellings of various
sizes, thereby Fathbh allChromosome form necklace
studded BalhbatPhase 2 duplication
ZygotenShorten
chromosomes and increases the intensity and approaching each problem in pairs
فيلتقي all identical كروموسومينWith
each other and begin the process of double points between Alkromusuman and
quickly extends to other areas,Note
that a Alkromusuman from the father and one from the mother at all, this process
is called bilateral double بالكروموسومات.3 Phase macrophages (Alngz)
PachyteneContinue
chromosomes minors and Alngz and rally around each other and show each
chromosome is composed of linked Kromatid yenThe
central area Centromere and each pair or a pair contains four Kromatidat and
called the Quartet,Then
begin the process of whirling and genuine interdependence between Kromatidin in
the group and does not relate to or wrap more than two with each
other.4 Phase Alanfrajah
(Altdhaafeeh) DiploteneChromosomes
begin to move away a little from each, Vtnfsal except areas which gets docking
between KromatidThe
first and last chromosome of the second chromosome transforms the second shape
to form تصالبي if contact one districtOnly
to form loop if contact Bmntqtin or if contact several regions.Every
point of contact between Kromatidin called decussation Chiasma contact zones
between Kromatidat opposite كروموسومينParticularly
important in the transition and the diversity of genetic makeup as exchange
parts of the sites second Alkromatid, this process is called
"transit".5 stage Altnavria
Owaltstatah DikanesDisharmony
continues and disappears cruciate shape at this stage and keep bilateral
chromosomes close togetherAnd
disappear nucleolus and nucleus membrane disappear begins moving pairs of
chromosomes to Planer cell areaThe
filaments are organized spindle extending from the poles of the
cell.B
metaphase I MetaphaseLiberated
chromosomes within the nucleus and be completed yarn spindle formation and lined
with pairs of identical chromosomesIn
the equatorial level of the cell, and each pair consists in this case of two
chromosomes identical or four half-chromosomal (4 Kromatidat),Every half symmetric
chromosome linked by centromere. Only
natural that the number of pairs of identical chromosomes equal to half the
number of chromosomes in the cell.C
anaphase I AnaphaseAt
this stage takes each chromosome Alkromusuman alleles in separation than other
shrink yarn spindleThus
turning a Alkromusuman to one pole of the cell and the second to the other pole
and bringing at each pole of the polar cell halfThe
number of chromosomes in cell origin (each chromosome component of
Kromatidin).D
telophase I TelophaseIn
this phase at each pole consists of polar cell membrane surrounds nuclear
chromosomes so composed Nouattan BnuetanEach
containing half the number of chromosomes in the original cell then At_khasr
cytoplasm until they are configuredTwo
separate cells (each chromosome contains Kromatidin).Meiosis II:A
complete split cells Alnatjtin of meiosis I to two new cells in a way
thatSimilar
to what is happening in that division indirect according to the following
phases:A)
prophase II rophaseB) metaphase II
MetaphaseC) anaphase II AnaphaseD) the final phase of
the second TelophaseA second
prophase:Central
body is divided into each cell to two tend to the poles of the cell where clues
configuration starts spindle and the wall disappearsNucleus
chromosomes show is made up of chromosomes each one consisting of a pair of
chromatidLinked each Psontromer and
oneB metaphase
II:Tstafkhalalha
chromosomes on the equatorial line of the cellC anaphase II:Centromere
splits which connects Kromatidi each chromosome to each other, and thus
inseparableAlkromatidan
and moving away in the direction of the electrodes.D telophase II:Gather
a group of chromatid (now a stand-alone chromosomes) at one pole of the
cell,Then
mutant تستطيل to high-twisted yarn, and composed around the nuclear membrane,
and thus consisting Khalatan containing NouattanEach
contain half of the genetic and the result is four cells each containing
halfChromosomes in the mother
cell.Ohmahalanksam
reductionist:1
consists of the final output of the four respective cells genetic half dubbed
the gametes (sperm, eggs).If
gametophyte united with the female gametophyte produces a zygote which contains
the original number of genetic traits which results in himEmbryo thus keep a
fixed number of chromosomes.2
exchange genetic traits between chromosomes fixed system and connective stage of
prophase I soTransmitted
recipe somewhere other recipe like this process is called cross.3
recipes appear prevalent and recessive
traits.
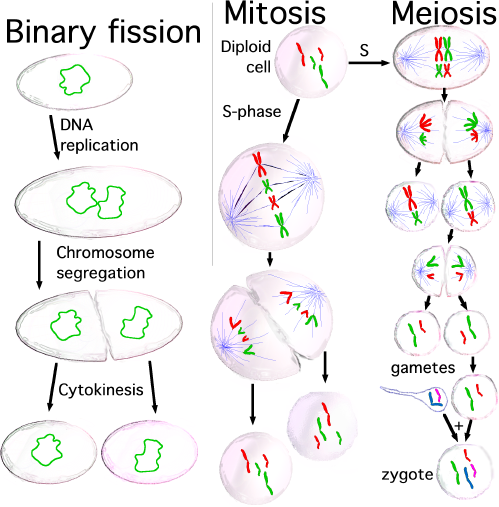
Here's division steps photographerTable of the main differences between indirect division (METOSIS)
And meiosis (MEIOSIS)
Split direct ................................................ .. .. Meiosis
Leads Elytkoan two cells are alike and Seeing ......... Leads to the formation of four cells is genetically similar.One Atdmannanksama. ...................................... Includes Anksamin consecutive ........................Not lead to halving the number of chromosomes .............. Lead to halving the number of chromosomes. ........Occurs in all members of the organism ..................... Occurs only in genital ..................Prophase relatively short Aanksm ................... Prophase long and passes through multiple stages.Aanksm to multiple stages ............................................ .............................................There is no transit operation are also not genetic ............. Characterized by the presence of the transit process and the emergence of genetic ........Pelletizing intersection points ......................................... Intersection points ........................................... ...... Centromere splits in metaphase ............. Centromere splits in the first metaphase.Takes to happen since the formation of the zygote .................. Takes to occur after puberty only in higher organismsAnd continues throughout the life of the object ............................................ .................................................. ......
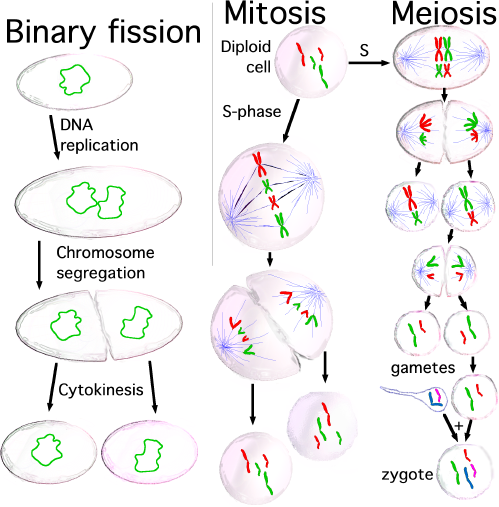
Here's division steps photographerTable of the main differences between indirect division (METOSIS)
And meiosis (MEIOSIS)
Split direct ................................................ .. .. Meiosis
Leads Elytkoan two cells are alike and Seeing ......... Leads to the formation of four cells is genetically similar.One Atdmannanksama. ...................................... Includes Anksamin consecutive ........................Not lead to halving the number of chromosomes .............. Lead to halving the number of chromosomes. ........Occurs in all members of the organism ..................... Occurs only in genital ..................Prophase relatively short Aanksm ................... Prophase long and passes through multiple stages.Aanksm to multiple stages ............................................ .............................................There is no transit operation are also not genetic ............. Characterized by the presence of the transit process and the emergence of genetic ........Pelletizing intersection points ......................................... Intersection points ........................................... ...... Centromere splits in metaphase ............. Centromere splits in the first metaphase.Takes to happen since the formation of the zygote .................. Takes to occur after puberty only in higher organismsAnd continues throughout the life of the object ............................................ .................................................. ......

No comments:
Post a Comment